2023/12/01
In 2024, the maritime industry will grapple with diminished demand and oversupply, potentially instigating intense competition, diminished profits, and plausible mergers and acquisitions. While container schedule reliability is enhancing, enduring challenges persist. Predicted blank sailings will escalate in response to market volatilities, whereas imbalanced container availability, propelled by economic crises, may persist in certain regions.
The container shipping industry, for its cyclical nature, witnessed an extraordinary peak in 2021 and H1 2022, punctuated by record levels and robust profits for shipping companies. However, a seismic shift occurred in 2023 as consumers curtail their investments in high-value goods, aligning with a global economy grappling with inflationary shocks and rapid rate hikes. This precipitated a drastic decrease in demand, culminating in a swift fall in spot rates on major trade routes.

In 2023, container trade recoiled due to deteriorating market conditions. The surge in vacant container stockpiles during the latter part of 2022 was an early harbinger of the decline, exacerbated by advanced ordering to secure timely deliveries. A fusion of more rational consumption patterns and destocking practices contributed to shrinking cargo volumes. Furthermore, European ports encountered setbacks due to sanctions levied on Russia. Preeminent European container hubs such as Rotterdam, Antwerp-Bruges, and Hamburg, serving as transshipment points to Russia, witnessed a plunge in container volumes and figures since the first half of 2023.
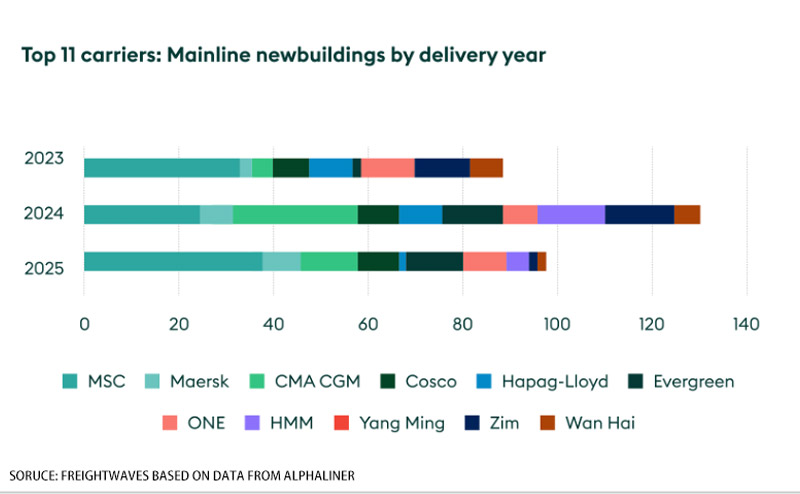
The tempo of deliveries accelerated this year, projected to augment throughout 2024, and remain robust in 2025. 2.48 million TEUs was slated for delivery this year, 2.95 million TEUs next year, and 2.26 million TEUs in 2025.
Geopolitical uncertainties in 2023 notably impacted the shipping industry, and these effects are projected to endure in 2024. The Russo-Ukrainian conflict instigated the closure of Black Sea ports, producing congestion and delays in goods transportation. On the heels of Russia's withdrawal from the Black Sea Grain initiative in July 2023, Ukraine's exports decelerated, eliciting price surges. While a promising global forecast has infused some stability into prices, the global food supply remains precarious due to the war and Russia's blockade of Black Sea ports, impeding Ukraine's capacity to export grains and food products to the global marketplace.
Strategic geopolitical uncertainties in 2023 noticeably disrupted the shipping sector, and these repercussions are projected to persist into 2024. The Russian-Ukrainian confrontation instigated the closure of Black Sea ports, engendering congestion and delays in goods transportation.
The Israel-Palestinian disagreement has also influenced the maritime industry, with global corporations issuing warnings and tweaking their operations. The schism poses hazards to crucial shipping routes, inclusive of the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz. The extent of its impact in 2024 hinges on the conflict's scope and duration, perpetuating uncertainty in the shipping industry.
The emergence of BRICS, now encompassing Saudi Arabia, Iran, Ethiopia, Egypt, Argentina, and the United Arab Emirates, is poised to diversify trade corridors, introduce alternative payment schemes, and enrich infrastructure evolution. Energy collaboration and resource rivalry may reshape shipping dynamics. The resolution hinges on how BRICS leverages its augmented influence in the evolving global landscape, proffering both opportunities and challenges for the shipping sector.